Unofficial cli tool for ZenHub.io
zhb is a command-line interface tool for ZenHub.io. With zhb, you can get, update or clear the parameters such as pipelines, estimates or +1 of the issue.
ZenHub has no public API at the moment. zhb uses internal APIs of the ZenHub chrome extensions arbitrarily. So interface of the commands would be changed.
$ go get github.com/cou929/zhb
$ go install github.com/cou929/zhbzhb issue <issue_number>
zhb transfer <issue_number> <pipeline_name>
zhb estimate <issue_number> <estimate_value>
zhb clearEstimate <issue_number>
zhb pipelines
zhb events [--page=<page_number>]
Show details of the issue. The example below gets information of issue 1 and uses jq command to handle json response. zhb find and show estimates, pipelines and +1 of the issue.
$ zhb issue 1 | jq '.'
{
"estimateValue": 5,
"issueNumber": 1,
"pipelineId": "1234567890",
"pipelineName": "New Issue",
"pluses": [
{
"Id": "1234567890",
"Comment": -1, # -1 means the `+1` is for entire issue, not for specific comment
"ZenhubUserId": "1234567890",
"GithubUserId": 1234567890,
"UserName": "user_name",
"CreatedAt": "2015-09-01T00:00:00.000Z"
}
]
}Transfer the issue to the pipeline. The example below transfers issue 1 to To Do pipeline. zhb exits with code 0 if the execution finished successfully.
$ zhb transfer 1 "To Do"Set the estimate value to the issue. The example below set estimate value 5 to issue 1. zhb exits with code 0 if the execution finished successfully.
$ zhb estimate 1 5Clear estimate value of the issue. The example below clears estiamte value of the issue 1. zhb exits with code 0 if the execution finished successfully.
$ zhb clearEstimate 1Show all pipelines. The example below uses jq command to handle json response.
$ zhb pipelines | jq '.'
[
{
"Id": "1234567890",
"Name": "New Issues"
},
{
"Id": "1234567890",
"Name": "To Do"
},
{
"Id": "1234567890",
"Name": "Done"
}
]Show events of ZenHub activities. The example below gets page 2 of events and uses jq command to handle json response. --page option is optional and default value is 1.
$ zhb events --page=2
[
{
"id": "1234567890",
"actor": {
"id": "1234567890",
"github": {
"id": 1234,
"username": "user_name",
"avatarUrl": "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/000?v=3"
}
},
"type": "transferIssue",
"repoId": 1234,
"organization": "org",
"repository": "repo",
"issue": 123,
"comment": 0,
"recipient": 0,
"createdAt": "2015-01-01T00:00:00.000Z",
"srcPipelineName": "New Issues",
"destPipelineName": "To Do"
},
...
]export ZHB_AUTH_TOKEN=<Your zenhub auth token>
export ZHB_ORG=<Your github organization name>
export ZHB_REPO=<Your github repository name>
export ZHB_REPO_ID=<Your github repository name>You can overwrite there variables through command line options.
zhb --org="another org name" [command]At the moment zhb has no way to authorize ZenHub account. So you should get your auth token from browser session which is authorized.
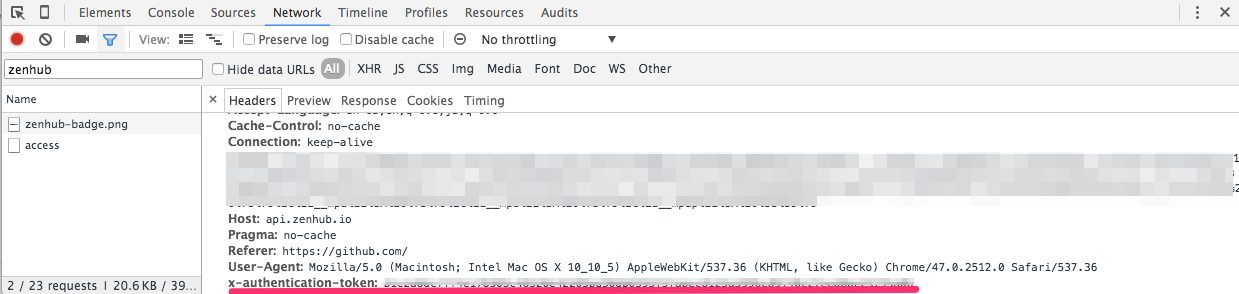
You can find out auth token by below steps:
- Open the developer tool.
- Open the
Networksection. - Add fileter
zenhubto eliminate all other requests. - Open your repository root page on GitHub.
- Open the
accessrequest. - You can see
x-authentication-tokenrequest header. The value of it isauth token. Just copy it.
Repository Id of GitHub is needed by +1 APIs of ZenHub. So you must set the variable to handle +1. You can omit this variable if you do not need +1 information. zhb just ignore +1 APIs if ZHB_REPO_ID is not presented.
You can find out Repository Id by GitHub Repository API. Below is an example to get ids and names of repositories by using curl and jq command.
curl -H "Authorization: token <your github auth token>" https://api.github.com/orgs/<your_org>/repos | jq '.[] | {id, name}'- Fork (https://github.com/cou929/zhb/fork)
- Create a feature branch
- Commit your changes
- Rebase your local changes against the master branch
- Run test suite with the
go test ./...command and confirm that it passes - Run
gofmt -s - Create a new Pull Request